Understanding Solar Generators
Solar generators are eco-friendly power sources that capture solar energy and store it in high-capacity batteries. They provide electricity without gas, noise, or harmful emissions, making them ideal for off-grid scenarios and emergency backup power.
How Solar Generators Work
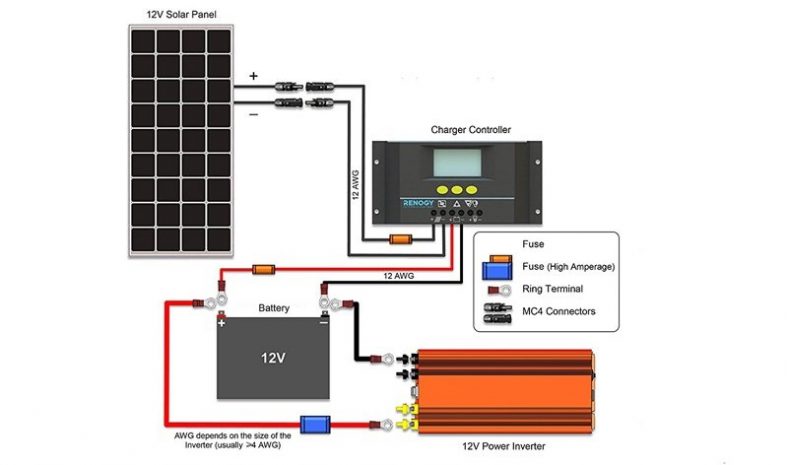 These systems convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic panels. This energy is stored in a battery, then converted from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) via an inverter—ready to power everyday electronics and appliances.
These systems convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic panels. This energy is stored in a battery, then converted from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) via an inverter—ready to power everyday electronics and appliances.
Components of Solar Generators
- Solar Panels: Convert sunlight into electrical energy
- Battery Storage: Stores energy for use when sunlight isn’t available
- Inverter: Transforms stored energy into usable AC power
- Charge Controller: Protects the battery from overcharging
- Ports and Outlets: AC, USB, and DC outputs for device compatibility
Evaluating Off-the-Grid Capabilities
Modern solar generators can support essential loads like lighting, communication devices, small refrigerators, and medical equipment—making them suitable for both short-term and long-term off-grid use when planned properly.
Energy Independence Through Solar Generators
These systems empower users to live sustainably and independently from the grid. Whether used in tiny homes, remote cabins, or while traveling, solar generators help cut ties with unreliable or expensive power sources.
Limitations and Challenges
- Performance varies with sunlight availability
- High-wattage appliances may require larger systems
- Charging times can be long without ample sunlight
- Initial costs can be high for full-featured systems
Integration and Application

Solar generators integrate into both standalone setups and hybrid systems. Many users combine them with existing solar panel installations or use them as mobile power stations for RVs, boats, and field operations.
Residential Use of Solar Generators
Homeowners use solar generators to keep refrigerators, lights, routers, and fans running during outages. They’re especially useful in disaster-prone or off-grid areas and often supplement rooftop solar systems.
Commercial and Emergency Applications
In healthcare, construction, and disaster relief, solar generators provide uninterrupted power for mission-critical tools. Portability and zero emissions make them especially valuable in temporary or outdoor settings.
Improving and Innovating Solar Generator Technology
In 2025, solar generator innovations include faster charging, better energy monitoring via apps, and improved battery chemistry (like LiFePO4). These changes enhance both performance and lifespan.
Advances in Solar Technology
- Smart app integration with live monitoring
- Stackable battery expansion modules
- Lightweight solar panel kits with foldable design
- Higher-efficiency inverters for cleaner AC power
Future Trends in Solar Energy Storage
Expect to see larger capacity batteries, ultra-fast solar charging, and AI-based energy optimization. Integration with home automation systems will also make solar generators even more user-friendly.
Costs and Return on Investment
While the initial cost can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, solar generators often pay for themselves by avoiding fuel costs, utility bills, and emergency generator expenses.
Solar Generators vs Gas Generators
- Solar: Clean, quiet, low-maintenance, higher initial cost
- Gas: Higher running cost, noise, and emissions
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can a solar generator run a house?
A: It can power essential devices, but whole-house use requires a large system with high capacity.
Q: Are solar generators good for long-term use?
A: Yes, especially models with LiFePO4 batteries, which offer thousands of charging cycles.
Final Words
Solar generators are no longer niche devices. In 2025, they offer real off-grid power solutions that are sustainable, portable, and increasingly affordable. Whether you’re preparing for emergencies or stepping into off-grid living, they provide peace of mind, energy freedom, and a cleaner footprint.

